Blog
From Neurons to Euphoria: The Intriguing Science of Magic Mushroom Effects
Magic mushrooms, known scientifically as psilocybin mushrooms, have captivated human curiosity for centuries with their profound effects on perception, consciousness, and emotions. The active compound in these mushrooms, psilocybin, has sparked a renaissance in psychedelic research, shedding light on the fascinating science behind their mind-altering properties. In this magazine-style blog, we embark on an enlightening journey to explore the intriguing science of magic mushroom effects, from their interaction with brain neurons to the euphoric experiences they induce.
Unraveling the Brain’s Serotonin System
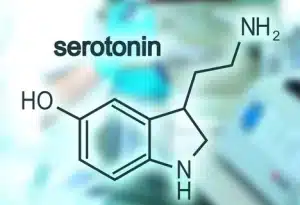

At the heart of the captivating effects of magic mushrooms lies the brain’s intricate serotonin system. Serotonin, known as the “happy neurotransmitter,” plays a crucial role in regulating mood, cognition, and perception. Psilocybin, the active compound found in magic mushrooms, shares a striking structural resemblance to serotonin. When ingested, psilocybin interacts with the brain’s serotonin receptors, with a particular affinity for the 5-HT2A receptor. This interaction sets off a fascinating cascade of events that lead to altered neural activity and, ultimately, the psychedelic experience. As psilocybin binds to the 5-HT2A receptor, it triggers a series of changes in neural communication, disrupting the typical patterns of brain activity. This disruption, in turn, leads to the characteristic effects of magic mushrooms, such as altered perception, vivid sensory experiences, and changes in thought patterns. Understanding the interplay between psilocybin and the brain’s serotonin system offers valuable insights into the mechanisms behind the mystical effects of magic mushrooms and underscores the significance of the brain’s neurotransmitter systems in shaping our conscious experience. As scientific exploration into the serotonin system continues, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intriguing world of psychedelics and their potential impact on our understanding of consciousness and mental health.
Magic Mushrooms and Neural Connectivity

The influence of psilocybin on the brain’s neural connectivity is a fascinating subject that has captivated the interest of researchers and enthusiasts alike. Utilizing sophisticated brain imaging techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), scientists have begun unraveling the intricate effects of psilocybin on neural communication. What emerges is a picture of a brain in a state of hyperconnectivity, where regions that do not typically interact are now engaged in heightened communication. This “hyperconnected” state is thought to underlie the characteristic effects of magic mushrooms, such as synesthesia—a merging of the senses where colors may be tasted, and sounds may be seen. Additionally, the perception of time undergoes a profound shift, leading to experiences of time dilation or distortion. Furthermore, emotions intensify, and individuals may report profound emotional experiences, ranging from euphoria and awe to introspection and catharsis. This hyperconnectivity fosters a unique and altered state of consciousness, offering a glimpse into the extraordinary potential of psilocybin to rewire neural pathways and reshape the way we perceive and experience the world around us. As researchers continue to probe the complexities of magic mushroom effects on neural connectivity, the deeper insights gained can contribute to our understanding of human consciousness and the brain’s remarkable capacity for adaptation and transformation.
The Default Mode Network and Ego Dissolution


The Default Mode Network (DMN) is a crucial brain network that plays a significant role in shaping our sense of self and self-referential thoughts. It is involved in the processing of autobiographical information, daydreaming, and mind-wandering. When individuals consume psilocybin, the active compound in magic mushrooms, the DMN’s activity is temporarily suppressed, leading to a fascinating phenomenon known as “ego dissolution.” During ego dissolution, individuals may undergo a profound and transformative experience, characterized by a dissolution of their sense of self and a feeling of unity with the surrounding world. Boundaries between the self and external reality seem to fade away, and a deep sense of interconnectedness with others and the universe takes over. This altered state of consciousness can be both awe-inspiring and humbling, as individuals may gain a new perspective on their identity and their place in the world. The experience of ego dissolution is often described as a spiritual or mystical encounter, where a profound sense of oneness and interconnectedness prevails. Researchers believe that this altered state of consciousness facilitated by psilocybin and the temporary suppression of the DMN may offer insights into the nature of human consciousness and open new avenues for therapeutic applications in mental health and personal growth. As scientists continue to delve into the intriguing relationship between magic mushrooms, the DMN, and ego dissolution, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the human mind and its potential for profound transformation through psychedelic experiences.
Neuroplasticity
The intriguing potential of magic mushrooms goes beyond their mystical allure; recent scientific research has unveiled their promise as a powerful tool for therapeutic applications. One fascinating aspect lies in their ability to promote neuroplasticity, the brain’s remarkable capacity to reorganize and form new neural connections. Psilocybin, the active compound in magic mushrooms, appears to play a crucial role in facilitating this neuroplasticity. Studies have shown that psilocybin can lead to increased synaptic plasticity, the process by which neurons form and strengthen connections in response to experiences and stimuli. This phenomenon is particularly noteworthy in the context of mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). In clinical trials, psilocybin-assisted therapy has demonstrated remarkable promise in helping individuals confront and process emotional trauma in a transformative and therapeutic manner. By facilitating neuroplasticity, psilocybin may enable individuals to gain fresh perspectives, break free from rigid thought patterns, and achieve long-lasting improvements in mental well-being. The potential of magic mushrooms as a catalyst for neuroplasticity has sparked renewed interest in the field of psychedelic-assisted therapy, offering hope for those seeking alternative and effective treatments for their emotional and psychological struggles. As research in this area continues to advance, the therapeutic potential of magic mushrooms may pave the way for groundbreaking advancements in mental health care and open doors to new dimensions of healing and self-discovery. However, it is essential to approach these therapeutic experiences with the guidance of trained professionals in controlled and safe settings, ensuring the utmost care and well-being of those seeking this transformative journey of healing and growth.
The Captivating Science of Magic Mushroom Effects
The science of magic mushroom effects is a captivating journey into the intricate workings of the human brain and its interaction with psilocybin. From unraveling the brain’s serotonin system to exploring the neural connectivity and ego dissolution induced by psilocybin, researchers continue to unlock the secrets of these mystical mushrooms. As we gain a deeper understanding of their effects, the therapeutic potential of magic mushrooms becomes increasingly evident, offering a glimmer of hope for those seeking relief from mental health conditions. However, it is essential to approach the use of magic mushrooms with caution and in controlled settings, guided by trained professionals, to ensure safe and meaningful experiences. As science continues to delve into the captivating realm of magic mushroom effects, we may yet uncover even more about their potential to transform our understanding of consciousness, perception, and mental well-being.


